スピーカーのインピーダンスが低すぎると良くないのはなぜですか?質問への回答
インピーダンス、オーム、およびカーオーディオまたはホームオーディオスピーカーに関するすべてについて話すと、混乱する可能性があります.ええ、ほとんどの人はスピーカーやオーム定格などに精通していますが、それは実際には何を意味するのでしょうか?
正確になぜ スピーカーのインピーダンスが低すぎるとよくないですか? それが私がここで答えるものであり、一度だけ片付けます。
この記事では、知っておくべきことをすべて取り上げます。
- 正確にはとは スピーカーのインピーダンス?
- スピーカーのインピーダンスが低いと良くない 2 つの大きな理由と、それが重要な理由
- なぜできるのか 高インピーダンスのスピーカーを使用するが、使用しない 下位のもの (および期待されること)
カバーすることがたくさんあるので、すぐに始めましょう!
スピーカーにとってのインピーダンスとは?スピーカーオームの説明
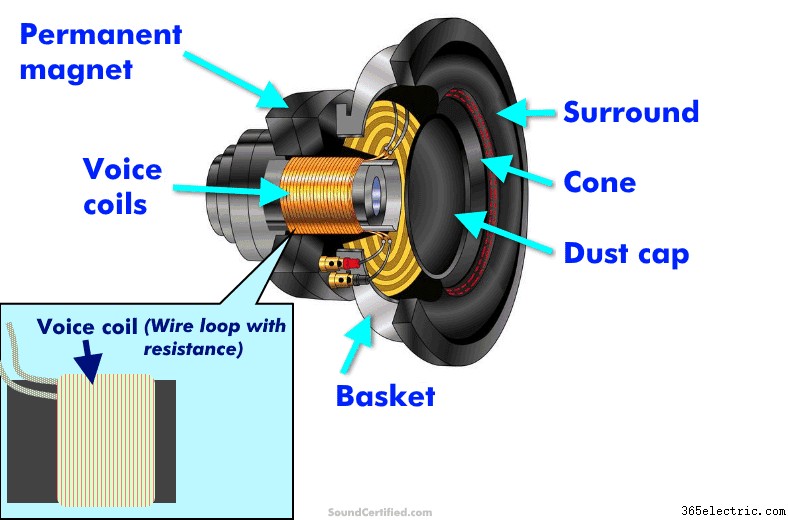
ボイスコイルを含むスピーカーを構成する部品の図。ボイスコイルは、使用される導電体から一定量の抵抗を持つ、きつく巻かれた長いワイヤです。スピーカー コーンを前後に駆動する磁場を生成し、空気の動きに合わせて音を生成します。
電気と電子の世界では、役に立つ仕事をするためにいくつかのことが必要です:
- 抵抗器やモーターなどに電流を流し、何か有用なことを行うための電圧を備えた電源。家庭用または車載用のアンプまたはラジオがこれを提供します。
- 電流が流れる経路を作るための導電体 (スピーカー ワイヤ)
- ある程度の耐性 流れる電流の量を制限します (電流が多すぎると、物が燃え尽きたり、熱くなったりします)
同様に、他の電気機器と同じように、スピーカーは小さなモーターのようなもので、流れる電気を使って動き (コーン) を音に変えます。基本的にはスピーカーがすべてです!
スピーカーのインピーダンスとは?
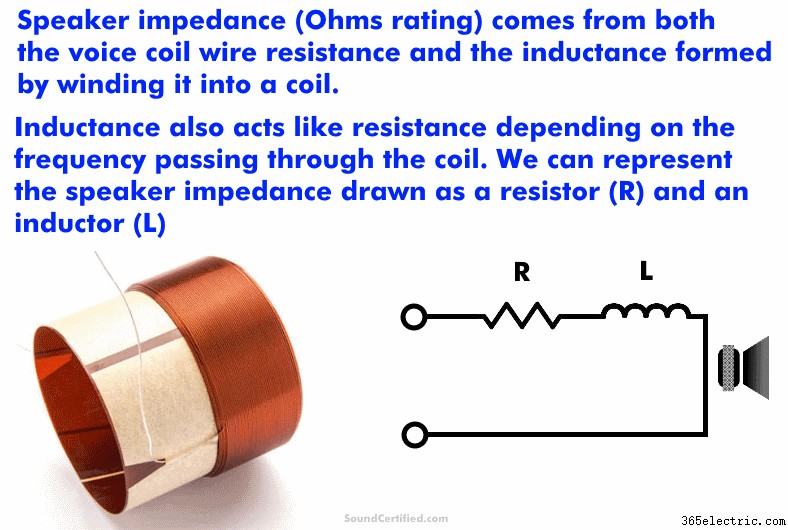
スピーカーのインピーダンスは、オームと呼ばれる抵抗の単位で測定され、合計 スピーカーが電気の流れに対して持つ抵抗の量。
スピーカーのインピーダンスは次の 2 つの要素から生じます:
<オール>バッテリーを短絡させてはいけないのと同じように、アンプやステレオにもある程度の必要があります ラジオまたはアンプが供給しようとする電流量を制限するスピーカー抵抗の量。
スピーカーのボイスコイルは非常に長いワイヤーを使用しており、コーンの動きを生み出すために磁場を生成するために必要なボイスコイルにしっかりと巻き付けられています。この長さのため、スピーカーのインピーダンスを構成する一部である一定量の抵抗が常に存在します。
特定のスピーカーの抵抗は、ほとんどの場合、オームで測定された数単位の抵抗です。
インダクタンスとは?スピーカーで重要な理由

インダクタは、インダクタンスを利用した非常に便利な電気部品です。インダクタンスは、ワイヤ ループを流れる電子と、それによって形成される磁場の特性です。同様に、スピーカーにはボイス コイルによるインダクタンスがありますが、少量です。
ワイヤのコイルには、ワイヤの直線部分とは異なり、興味深い副作用があります。ボイス コイルの巻線は、インダクタンスと呼ばれる電気的特性を持つループを形成します。 音楽信号のような交流周波数がインダクタンスを持つコイルに適用されると、磁場が存在するため、電流の流れが妨げられます。
This is called inductive reactance and it’s different from resistance as it changes as the frequency changes; resistance stays the same.
For speakers, this matters because it means that the total resistance is made up of the two things I mentioned:wire resistance and inductive reactance. The name used to describe this total is impedance.
For speakers, this means that impedance (the total resistance) changes slightly as music plays because of the changing sound frequencies. However, the good news is that we can still categorize speakers according to an Ohms rating since it’s always pretty close.
When we talk about the impedance of a speaker, most of the time people are referring to the range of the speaker assigned to categories like 2 ohms, 4 ohms, 8 ohms, and so on. This is how we match speakers to a car or home amplifier, radio, and so on.
In the electrical world, resistance units measured in Ohms can be written as the Greek symbol Omega, or “Ω.”How does speaker impedance work?
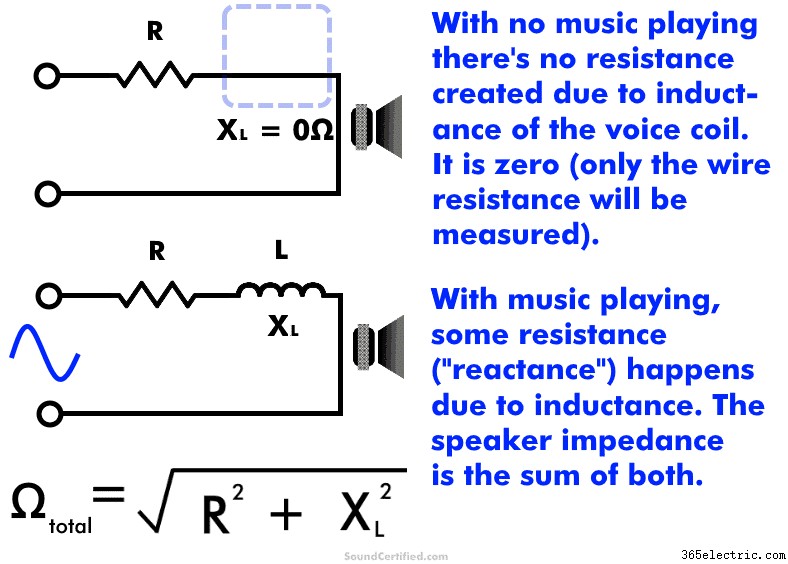
When a musical signal (made up of alternating current) is applied to a speaker it generates magnetic fields as current flows through the tightly wound wire coil. Interestingly enough, a coil of wire develops magnetic fields that resist the flow of the current (resistance, also called reactance in this case).
Similarly, many other electrical components like motors deal with the same electrical resistance as alternating current (AC) is applied.
How the math works (yeah, it’s a little complicated!)
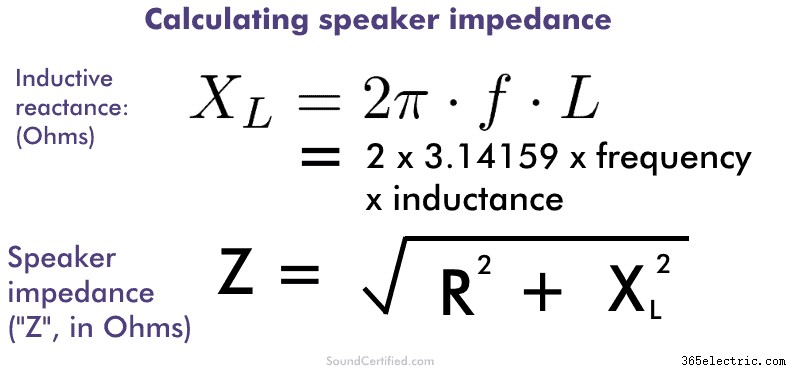
Because of how inductance works and the physics involved, the speaker “impedance” (total resistance) isn’t the sum of the resistance and the inductive reactance. Instead it’s the “algebraic” sum, meaning it’s the square root of the sum of the squares. You may remember this kind of math from trigonometry class.
Speaker impedance isn’t as simple as just adding the measured DC resistance of the coil wire and the inductive reactance for a given frequency.
Instead, speaker impedance is found from the algebraic sum of the coil’s wire resistance and inductive reactance. You can find this by squaring each and then taking the square root of the two numbers added together.
Inductive reactance is commonly written as “Xl”, pronounced “X sub L” and is measured in units of Ohms just like resistance. Inductance is measured using a unit called the “Henrie” and commonly noted with an “H”:“uH” for microHenries, “mH” for milliHendries, and so on.
There’s also a corresponding value for capacitors called capacitive reactance (Xc) but that doesn’t usually apply for speaker voice coils. It’s very important for speaker crossovers, however.
Why is it bad if speaker impedance is too low?
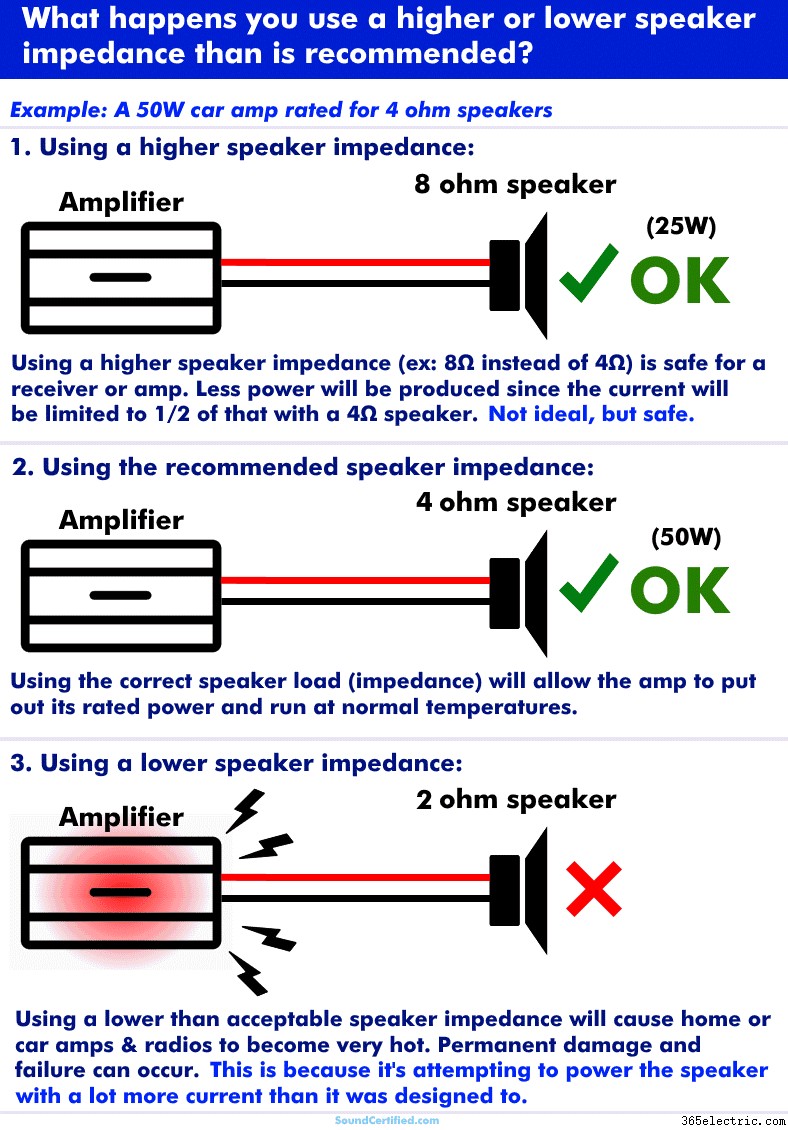
Just like any other device connected to an electrical power source, the speaker impedance will determine how much or how little current a home or car receiver, amplifier, etc will produce. The speaker impedance also affects how some speaker components such as speaker crossovers behave too.
What happens if speaker impedance is too low?
You can connect a higher speaker impedance in most cases without any problems (at least not major ones). A radio, home or car amplifier, etc will still produce sound and run at normal or low temperatures. That’s because a speaker with a higher impedance than expected will reduce how much electrical current the audio source tries to produce.
As a side effect, you’ll get sound but with much lower power output than you would with the correct speaker load. Car stereos or amps, for example, have to work with lower voltages than home stereos so they need a lower impedance 4 ohm speaker typically to produce more power.
Home stereos, on the other hand, have higher voltage available and can use a higher speaker impedance (8 ohms, typically).
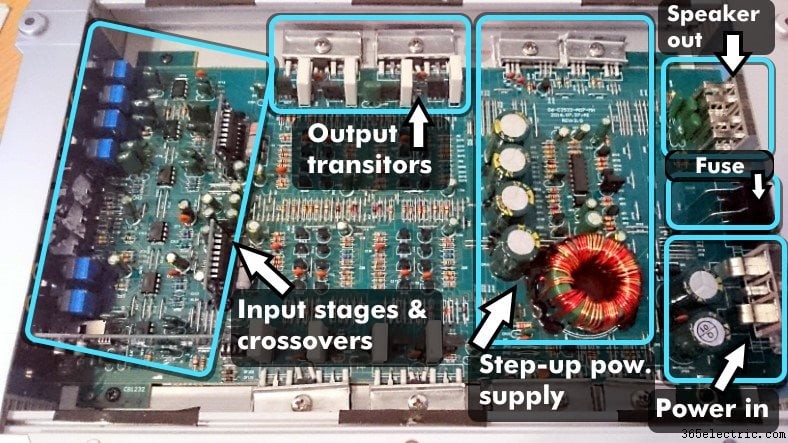
Internal view of an amplifier. When connected to a speaker impedance load that’s too low, the amp will begin to get very hot and this can burn out the output transistors as they can’t handle the heat caused by trying to supply excessive current to a lower speaker load.
However, using a lower speaker impedance is bad because it causes the radio or amp to attempt to put out twice as much (or more!) current than it’s designed for. Your home or car stereo will get very hot quickly and if you’re lucky will go into a self-protect mode and shut itself off.
However, in my experience, it’s pretty common for the output stage electronics to burn out when connected to a lower speaker load than they should be. The high-power transistors in a home or car amplifier or stereo are only rated for a certain amount of heat &electrical current.
When they’re forced to try and handle an amount outside that range they become super hot and start to break down permanently. It doesn’t take long before the damage is permanent and they no longer produce sound.
Caution! Never wire speakers in a way that gives a total speaker load lower than the radio or amp is rated for. Also, don’t guess about the correct speaker impedance – check first.I’ve seen cases where someone’s “friend who’s smart” has as a way to “get more power” but caused a stereo or amp to try to and put out more power than it was designed for. The end result was a burned-out amplifier.
Why does speaker impedance matter for crossovers?
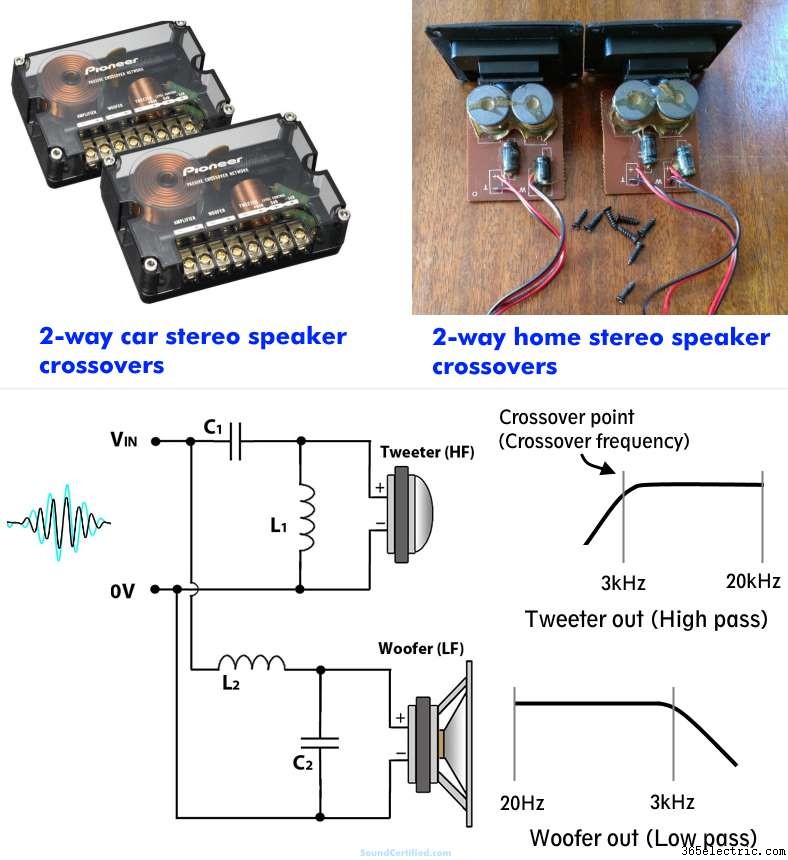
Speaker crossovers work to separate the sound sent to certain speakers for improved sound, reducing distortion, and to give you more control over how they’re used. For example, they block bass that tweeters can’t produce and highs that a woofer can’t produce well. However, they’re designed for a specific speaker impedance. Changing the speaker impedance affects the sound.
Speaker crossovers are amazingly helpful for getting better sound with speakers. Even the cheapest, most basic capacitor connected inline with a tweeter working as a high-pass filter makes a big difference in the sound.
The result is cleaner sound and avoiding possibly damaging it when bass sounds are played.
The catch is that because of how crossover components (capacitors and inductors) behave, they’re designed for specific speaker loads and can’t be used with other Ohm loads without affecting the sound output.
Crossover shift when using different impedance speakers
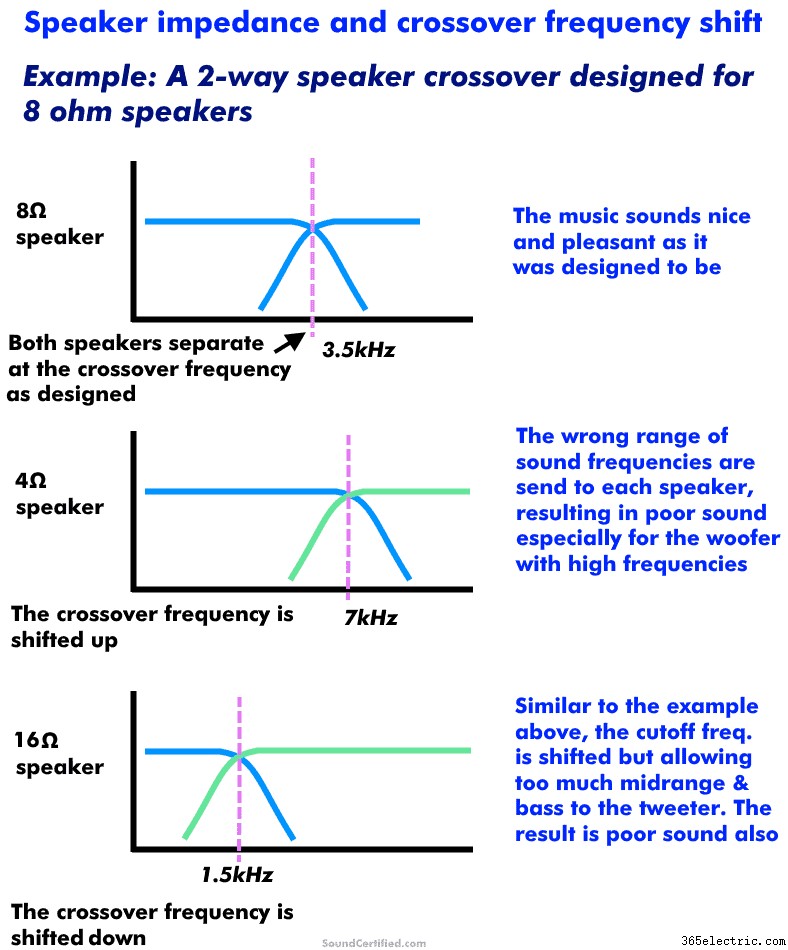
When you change the speaker impedance connected to a speaker crossover it can significantly shift the crossover’s cutoff frequency. As a general rule:
- Halving the speaker impedance (ex.:8ohms to 4 ohms) doubles the frequency
- Doubling the speaker impedance (ex:8 ohms to 16 ohms) halves the frequency
That’s bad because it allows the speakers to be sent a sound range they’re not suited for. In the case of tweeters, bass &midrange are bad because they can’t produce it properly. Similarly, many woofers can’t produce high frequency sounds well.
The end result in either case is poor sound that’s a lot worse sounding that it should be. If you change the speaker Ohms load you’ll have to replace the speaker crossover as you’ll need different parts values for it to work the same.
Is 8 or 4 ohm better? Is higher or lower impedance better for speakers?

8, 4, and 2 ohm speakers aren’t necessarily “better” than one another. The correct answer is that it depends on the application and what stereo or amplifier is being used. The best impedance is the one that matches an amplifier or stereo’s impedance spec correctly.
By industry tradition, 8 ohms are used for home and some theater speakers. 4 ohm speakers are generally used for car and marine audio, with some 2 ohm models also (usually subwoofers).
例:
- 8 ohm speakers are used in home stereo systems and require 1/2 the current of a 4 ohm speaker. That means they can use smaller speaker wire as they can take advantage of home electrical systems that have a high voltage supply for driving speaker amplifiers.
- 4 ohm speakers are used because car stereos and amplifiers (particularly car head units) can’t make large amounts of power in speakers as they have a very low 12V power supply. Reducing the speaker impedance from 8 to 4 means we can double the power for the same output voltage.
As a matter of fact, car stereos can only put out about a small 15-18 watts RMS per channel, despite the exaggerated peak power ratings you may see in advertisements. That’s because they only have about 12 volts to work with and have to divide that in half in order to produce AC waves that drive a speaker.
Car amplifiers are able to deliver huge amounts of power to 4 and 2 ohm speakers. They use an internal “inverter” power supply that steps up the +12V supply to higher voltages. This way they’re able to supply much more power to 2 or 4 ohm speakers than would be possible otherwise.
More great articles to see
Did you enjoy my article? There’s plenty more where that came from!
- Did you know? You can power a car amp in your home.
- Want to learn more about audio? Find out here how speakers work.
- Tweeters are great but sometimes are too loud. In this guide I’ll show you how to reduce tweeter volume the right way.
Check out my full line of how-to &info articles here.
