DSLR レンズの仕組み:DSLR レンズの説明
カメラレンズは間違いなく写真家のセットアップの最も重要な部分であり、ほとんどのプロの写真家は、最高品質のレンズを持っている限り、その逆ではなく、普通のカメラボディで撮影することを好みます.しかし、DSLR レンズの世界に足を踏み入れたばかりの場合、一見圧倒されるかもしれません。横にあるすべての数字と文字は正確に何を意味するのでしょうか?どのレンズを入手すればよいですか?また、レンズはどのように機能しますか?

魔法のように思えるかもしれませんが、実はとてもシンプルです。読み進めてください。
適切なレンズを選択すると、キャプチャしようとしている画像が成功または失敗する可能性があります。これは、レンズがカメラのセンサーに投影される画像を制御するカメラの一部であるためです。レンズがなければ、白色光しか捉えることができず、実際にはあまり役に立ちません.
特定の写真撮影状況に適したレンズを自信を持って選択できるようにするには、DSLR レンズが実際にどのように機能するかを理解することが非常に重要です。各レンズのコードのような刻印を解読できれば、各カメラ メーカーが作成する膨大な選択肢からどのレンズを入手するかを選択する際の頭痛の種が少なくなります。
カメラ レンズとは
どのカメラのレンズも、光を定点に焦点を合わせることができるシンプルなツールです。 DSLR では、この固定点はデジタル イメージ センサーです。これを行うために、実際のレンズはチューブのように見え、内側 (凹面) または外側 (凸面) に湾曲した複数のガラス板が含まれています。レンズの種類ごとに異なる数と配置のガラス プレートが含まれているため、さまざまな状況で画像をキャプチャできます。これらのレンズ要素は、基本的に光をさまざまな方法で曲げる役割を果たします。
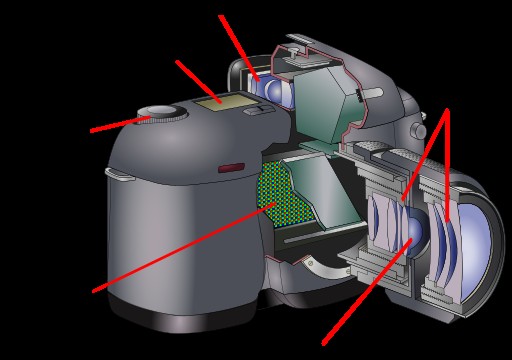
DSLR カメラ レンズの構造
カメラのレンズを機能させる科学は、実際にはかなりクールです。プリズムを使用して白色光をさまざまな可視色に分割するという小さな実験を行った学生時代を思い出すと、レンズはそれのより複雑なバージョンです.
通常、レンズの内側について心配する必要はありません。気になる整備部品はありません。ただし、レンズがどのように機能するかを本当に理解するには、DSLR レンズを実際に構成しているものを理解することが重要です。
レンズの前部には前部要素があり、後部には別の要素があります。これらの 2 つの要素は、基本的にレンズ内の残りのものを保護します。 2 つの要素の間にレンズ グループがあります。これは、光を集中させるのに役立つ凹凸ガラスプレートのシリーズです。レンズの内側には、光を取り入れる調整可能な開口部を制御するレンズの一部である開口部もあります。
dSLR (デジタル一眼レフ) カメラまたは SLR (一眼レフ カメラ) のファインダーを覗くと、レンズのガラス要素によって画像が変更されているように見えます。ミラーレス カメラには、この画像をビューファインダーに映すミラーがないため、これらのカメラを小型軽量化できます。
以下は、この特定のレンズ内の 9 つのガラス要素を明確に示す、蛍光レーザー イメージングを使用したペンタックス 1.4 レンズの切断写真です。
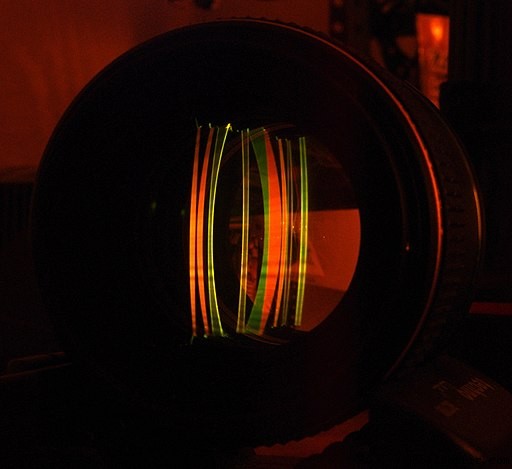

これらのパーツの一部は固定され、一部は画像のフォーカス、ズーム、安定化のために移動します。パーツの可動、固定、配置はレンズごとに異なります。
レンズの外側にもいくつかの異なる部品があり、レンズごとに、またメーカーごとに変更される可能性があります。レンズの前面には、円形フィルターを取り付けるフィルター スレッドがあり、続いてレンズ フード/シェードを取り付けることができるレンズ フード取り付け溝があります。
レンズ フードは、特に日当たりの良い環境では重要です。迷光ビームによるフレアやその他の望ましくない影響を防ぐのに役立ちます。
フィルター スレッドを使用すると、UV や偏光子など、さまざまな種類のフィルターを使用できます。フィルターには、レンズの直径に基づいてさまざまなサイズがあります。それらは 50mm から 100mm を超えるものまであります。ねじ込み式フィルターは簡単に外せず、レンズにぴったりのサイズで購入する必要があるため、レンズに取り付けられたフィルター ホルダーを使用するシングル サイズの正方形フィルターも人気があります。要素はそれほど問題ではありません。
多くの写真家はレンズ、特に高価なレンズに UV フィルターを使用して、ひび割れや引っかき傷など、硬いものにレンズがぶつかったときにレンズを保護します。私は個人的に、レンズが鋭利な物体にぶつかり、安価な UV フィルターが粉々になったことが何度かありました。もしそれがレンズ自体の前玉に起こっていたら、もっとひどいことだったでしょう.

レンズ本体の中央には、フォーカス リング、ズーム リング、レンズ仕様のマーキング、被写界深度インジケーター、絞りリング、手ぶれ補正コントロールなど、いくつかの異なる設定とパーツがあります。レンズの背面には、レンズをカメラ本体に取り付けるレンズ マウントがあります (カメラに適したタイプであることを確認する必要があります)。また、レンズの手動フォーカスと自動フォーカスを切り替えることができる「MF/AF」スイッチもあります。
距離インジケータは、被写体までの距離をフィートとメートルで示します。 DSLRS ではそれほど多くはありませんが、以前はすべてが手動で行われ、過焦点距離などを計算する必要があった場合、これは重要でした.
「USM」 の文字は超音波モーターを表し、これらのレンズは、モーターが焦点を合わせるのが速く、静かであるため、多くの人に好まれています。また、「HSM」または高速モーターとラベル付けすることもできます。
カメラ レンズの文字「DX」は、この記事で後述するクロップ センサー レンズを表します。 DX は Nikon の指定であり、EF-S は Canon レンズの指定です。
「Asph」という文字は非球面レンズを表し、基本的には一部のレンズが球面ではないことを意味し (症状のない無症候性と同様)、収差を制限するのに役立ちます。
画像安定化のマークは、少し混乱する人もいます。 VR は手ぶれ補正、IS は手ぶれ補正、OIS は光学式手ぶれ補正の略です。光学式手ぶれ補正は、デジタル手ぶれ補正よりも優れており、単なるデジタル画像処理ではなく、実際のフローティング ガラス要素が含まれます。
安定化は優れた機能であり、実に巧妙な機能です。最大 2 ストップ遅く撮影できるため、最低推奨シャッター スピード 1/125 秒で撮影する必要がなくなります。基本的にセンサーとモーターを使用して、手ぶれやその他の小さな動きを打ち消します。大きな動きには向いていません。
レンズマウントは、レンズをカメラに接続する場所であり、ほこりや汚れを入れずにしっかりと固定します。これらは現在、主に銃剣タイプです。ソニー、ニコン、キャノンなどの各メーカーには、独自のレンズ マウントがあります。後で説明するアダプターを使用すると、あるブランドのカメラ用に作られたレンズを別のブランドのボディで使用できます。
魚眼レンズなどの一部のレンズでは、実際にはレンズの後部にフィルター マウントがあります。これは、レンズの曲率が大きいため、フラット フィルターを前面に取り付けることができないためです。
DSLR レンズの仕組み
簡単に言うと、レンズ チューブ内の一連のガラス プレートによって、光がデジタル イメージ センサーに集束され、光が画像として記録されます。

レンズは、カメラセンサーで写真を撮ろうとしている被写体の画像を形成します。ここで、少し技術的な話をしましょう。それほど複雑ではなく、レンズの仕組みをよりよく理解できるので心配はいりません.
光が凸レンズを通過して画像を形成する際、入射角とガラス レンズ構造自体の影響を受けます。レンズまでの被写体距離が変わると、光の入射角も変わります。レンズから遠く離れた被写体の像は、レンズの近くに結像し、その逆も同様です。
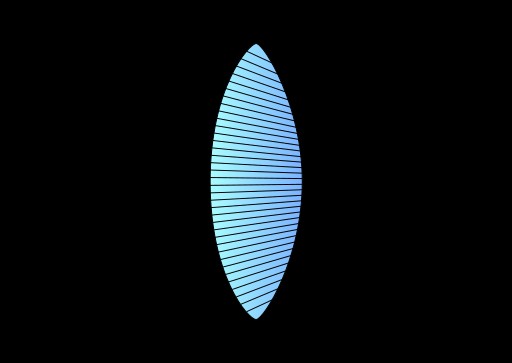 厚い凸レンズ (大きなお腹) は、さまざまなポイント間の距離が異なるため、光をより鋭い角度で曲げます。レンズが増えました。その結果、光はレンズの近くに収束します。凸レンズが薄いほど、像はレンズから離れて形成されます。これにより、画像のサイズが大きくなります。
厚い凸レンズ (大きなお腹) は、さまざまなポイント間の距離が異なるため、光をより鋭い角度で曲げます。レンズが増えました。その結果、光はレンズの近くに収束します。凸レンズが薄いほど、像はレンズから離れて形成されます。これにより、画像のサイズが大きくなります。
フォーカス
手動または自動でレンズの焦点を合わせる場合、レンズ要素の一部をカメラ センサー (一眼レフの場合はフィルム) に近づけたり遠ざけたりします。これは、レンズによって光が曲げられる方法を変更し、光線が収束する位置を再配置します。焦点を合わせたいオブジェクトが鮮明になるポイント、つまり光線がセンサーまたはフィルムのある場所に収束するポイントが見つかるまで、これを行います。マニュアル フォーカスは、何年もの間標準であったものです。現在、オートフォーカスと手動調整によるオートフォーカスが普及しており、それには正当な理由があります。
完璧ではありませんが、フォーカシング技術により、私たちが手動でリングを回すよりもアクション写真のフォーカシングがはるかに高速になりました.薄暗い光の中など、よく見えない他の状況では、デジタル センサーが目よりも優れている場合があります。
オートフォーカス
オートフォーカスは興味深い機能です。連続オートフォーカスやシングル オートフォーカス (通常はセレクター スイッチがあり、そのうちの 1 つはより多くのバッテリーを使用します) などのさまざまなオプションがある以外に、カメラがレンズに信号を送信したり、その逆の信号を送信したりすることによって機能します。フォーカス試行後に画像が鮮明になったという信号が返されると、カメラは仮想フォーカス リングをどちらの方向に回すかを認識します。このプロセスは、フォーカスが得られるまで繰り返され、説明したよりもはるかに高速です。
もう 1 つお気づきかもしれませんが、焦点を合わせるとレンズが長くなったり短くなったりしますが、そうでないレンズもあります。違いは、内部フォーカスと外部フォーカスです。
焦点距離
この長さは、レンズが無限遠に焦点を合わせているときに実際に計算されます。しかし、それは実際にはどういう意味ですか?光がカメラを通過すると、上下が反転します。画像が反転するポイント (光が収束するポイント) は、節点として知られています。その点からイメージ センサーまでの距離が焦点距離です。
これは文字通り、光が収束して撮影対象の鮮明な画像を形成するポイントとイメージ センサーとの間の距離です。通常はミリメートル (mm) で測定され、レンズに明確にマークされます。
焦点距離は、目の前にあるシーンがどれだけキャプチャされるか、シーンの各部分がどれだけ大きくまたは拡大されるかを示します。焦点距離が長くなるほど、画像はより「拡大」されます。一方、焦点距離が短いほど、倍率を下げてより広い視野を捉えることができます。
レンズの焦点距離は、レンズを購入するときに目にするものです。特定のレンズの倍率と、レンズと作成された画像との間の距離の両方です。したがって、1000mm レンズは 100mm レンズよりもはるかに拡大されます。比較的中立的なレンズが必要な場合は、焦点距離が 50 mm のレンズを使用できます。実際に得られる画像は、フル フレーム カメラまたはクロップ カメラのどちらを使用しているかによっても異なります。名前が示すように、倍率によるものではありません。
クロップセンサー/カメラは、このクロップのためにレンズの焦点距離を一見長くします。例として、Nikon APS-C センサーには 1.5 倍の拡大鏡があるため、同じレンズをそのようなカメラに取り付けると、同じレンズをフルフレーム カメラに取り付けた場合よりも画像が 1.5 倍大きくなります。鳥の詳細は必要ですが、風景のワイド ショットは必要ありません。
この乗数から、いわゆる等価焦点距離が得られます。そうすれば、別のタイプのカメラを使用した他の誰かのセットアップと比較して、特定のタイプのカメラクロップで使用する必要があるレンズを見つけることができます.
フルフレーム センサーは、35mm フィルムまたは 24mm x 36mm のサイズに相当します。クロップ フレーム センサーとは、35mm フィルム フレームよりも小さい任意のサイズのセンサーを意味します。クロップ フレーム センサーは、フレームの外側のエッジを切り取ります。つまり、周辺の画像にあるものは見えません。
フルフレームレンズは高品質であるため、価格と重量が高くなります。フルフレームカメラもそうです。多くの写真家が好むフルフレーム カメラ用のレンズも数多くあります。
レンズに戻ると、凸レンズ要素が多いほど角度が広くなり、焦点距離が短くなります(たとえば 35mm)。より平らなガラス エレメントを備えた望遠レンズでは、画角が狭くなり、焦点距離が長くなります (たとえば 200mm)。
非常に初期のレンズは単焦点距離しかありませんでした (現在は単焦点レンズとして知られています)。かなり賢い人々が、近くのものと遠くのものの写真を撮ることができるレンズが 1 つあればクールだと考えるまでは。彼らは、レンズ群の構成を変更できる方法を思いついたので、結節点がイメージセンサーからどれだけ離れているかを変更できます。こうして「ズームレンズ」が誕生しました。
絞り
絞り 写真用語の 1 つは非常に専門的で、理解するのに少し時間がかかることがあります。しかし、レンズを選んだら、思い通りのショットを撮るのがずっと簡単で楽しいものになります!
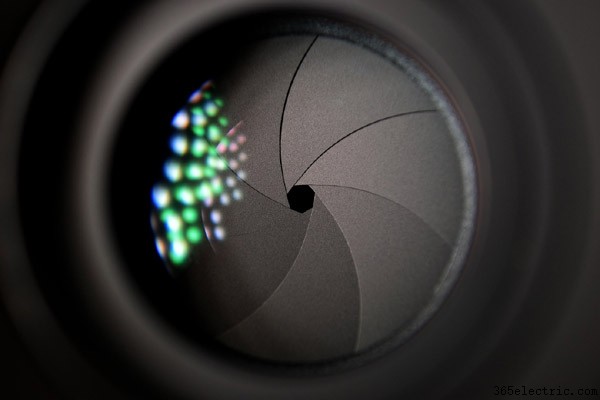
開口部は、光が入る開口部の大きさに関連しています。瞳孔の大きさを制御する虹彩 (目の色のついた部分) のようなものだと考えてください。絞りは絞り値で表されます (紛らわしいことに)数字が小さいほど、開口部が大きくなります。たとえば、f ストップが f/2.8 のレンズは開口部が大きく、f ストップが f/11 のレンズよりも多くの光を取り込みます。
F ストップには、多くの人がその意味さえ知らない面白い名前が付いています。それは実は先ほどお話しした焦点距離に関係しています。 F ストップは、焦点距離の単なる分数です。これらの分数の仕組みは次のとおりです。300mm f2.8 レンズ(素晴らしい明るいレンズ)があるとします。 f2.8 の絞り値で撮影するように設定されている場合、焦点距離 300mm を 2.8 で割ると 107mm になります。これはレンズの開口部のサイズです。
絞りは、画像の被写界深度、または画像全体がシャープで焦点が合っているかどうかにも影響します。高い数値の F ストップを使用すると、光の量が少なくなり、被写界深度が深くなります。低い数値の f ストップを使用すると、より多くの光が取り込まれ、被写界深度が浅くなります。
このパラメータを調整すると、人物だけにピントが合って背景がぼやけたクールなポートレートを作成するのに役立ちます。開口部を大きくする (または絞り値を小さくする) と、これを作成できます。一方、開口部が小さい (または f 値が大きい) と、より多くの画像に焦点を合わせることができ、風景に最適です.

レンズの絞りは、レンズに見られるもう 1 つのコードのような刻印です。レンズの焦点距離の横に記載されている絞り値が最大絞り値になります。最大 f 値が低いほど (そして開口部が広いほど)、レンズが暗い場所でより優れていることを意味します。したがって、夜間または自然光 (フラッシュなし) での写真撮影が得意な場合は、これは間違いなく考慮すべきことです。
低い F 値は、レンズの品質の指標でもあります。最高品質のレンズは焦点範囲全体で一定の f ストップを持ちますが、低品質のレンズ (および低価格) は焦点範囲を移動するにつれて変化する f ストップ (3.5-5.6 など) を持ちます。この場合、広角から望遠に焦点距離を移動すると、おそらく 1 ストップ程度の光が失われます。これらは可変開口レンズと呼ばれ、その他は固定開口レンズと呼ばれることもあります。
部品や機構が関係するため、可変絞りレンズは大きくて重くなります。一部のカメラ システムではレンズに絞りが組み込まれていませんが、これはまれであり、特別なレンズが必要です。
以下は、Think Media の説明です。これは、これらすべてを理解し、さらに詳しく説明するのに役立ちます。
カメラレンズとカメラ本体
写真家は常に、カメラ本体そのものよりも「ガラス」のコレクションについて話します。カメラが行ったり来たり。レンズが長持ちします。もちろん、これにはいくつかの制限があります。 1970 年代と 1980 年代のニコンの「防弾」レンズは、安価で高品質ですが、限界があります。多くはマニュアル フォーカスで、多くはオートフォーカス付きで長年使用されており、電源、レンズ マウント、コネクタなどを含めて消耗している可能性があります。しかし、ほとんど使用されていないレンズがまだ見つかる
これは、優れたデジタル一眼レフ レンズが毎年登場していないということではありません。新しい機能は多くないかもしれませんが (レンズに搭載できる機能は限られています)、技術の変化に伴い、軽量化、性能の向上、低コスト化が進んでいます。アマチュア写真家にとって非常に優れた品質の画像を提供する小型軽量の 50mm 単焦点レンズを約 100 ドルで入手できるかもしれませんが、光学的に安定した 100 ~ 300 mm の単焦点レンズに取って代わることはありません。
レンズ コレクションを始めるときに、Nikon や Canon など、さまざまなマウントのレンズを購入するという罠に陥らないように注意してください。 Nikonなどの1つのレンズマウントに固執し、カメラにCanonなどの他のブランドのレンズを使用できるアダプターを使用したい.これらのアダプターは年々改良されており、1970 年の Nikkor レンズを使用した機械的機能のみを提供する場合がありますが、最新のレンズではオートフォーカス、光、その他の測定値を提供する場合があります.
アダプターをテレコンバーターやマクロ リングと混同しないでください。これらは異なるマウントに適応するのではなく、レンズの動作に影響を与えます。テレコンバーターには、余分な光学要素による光の損失を引き起こしますが、全体の倍率/焦点距離を増加させる拡大係数を持つ光学要素があります。
Macro extension rings on the other hand are just spacers which allow you to put your subject much closer to the lens and still have focus. This is because the focusing range of your lens in decreased, no longer being able to focus at infinity.
Camera bodies are also replaced often (besides the fact that shutters dont last forever) because camera technology evolves so quickly. Camera manufacturers are in a high level of competition every year putting out new models that are better than last years, whether its the sensor, battery life, megapixel count, etc. Don’t forget that every time your camera body gets better, your existing lenses will also give you better photos when used along with it.
What you should keep in mind when buying new lenses if you are serious about photography due to what i described so far is you should buy good quality lenses with quality features, such as a low number fixed aperture. They will last if you take care of them, and you will be able to use them on different camera bodies.
While im on the topic of budget, third party lens manufacturers such as Sigma, Tamron and Tokina make lenses for other camera brands and these can save you quite a bit of money, while keeping image quality good. Always read lens reviews or try before buying, especially with third party manufacturers, to make sure you are satisfied with the photos.
Types of DSLR Lenses
Now that you have a greater understanding about how a DSLR lens works, understanding which lens is right for you and why will be an easier task. There are two main types of DSLR lenses:
Prime Lenses
These lenses have a fixed focal length meaning that you have to move around more when framing your shot. However, they are generally a much faster lens and produce a sharper image. They also tend to be lighter which is great for travelling.

Zoom Lenses
These lenses have a varying focal length meaning that you can zoom in and out of a scene without having to move your location. Their flexibility can be a great asset although they tend to be much bigger and heavier than prime lenses.
Zoom lenses work on the idea that you are moving various lens elements inside the lens with relation to each other, whether by turning the zoom ring or pulling it forward or back. This changes the focal length and the magnification power of the lens.

While prime lenses can help quickly develop your photographic skills, if you are not sure what kind of photography you will be doing, a zoom lens can be a great option. Within these two types of lenses there are several different more specialised lenses available. Again, depending on the type of photography you are going to be doing will depend on which lens you should choose.
Kinds of DSLR Lenses
Macro DSLR Lenses
These are the lenses that allow you to capture the tiny and intricate details of a scene. Often used in photographing small creatures such as ants and spiders, flowers as well as abstract images.

Macro lenses can be purposely built prime or zoom lenses or they can be classed as macro simply because their closest focusing distance is short. The prime macro DSLR lenses will usually have a wider aperture and higher quality glass than their zoom counterparts, therefore producing a higher quality image.
A more affordable option if you are just getting started is to choose a lens that also has a macro function. This means that you can still do your everyday photography but if an occasion to capture a macro image comes along there is no need to change the lens. On the other hand, these types of lenses often have a longer focal length which will lower the quality of the image.
Wide Angle DSLR Lenses
If landscape photography is your thing then wide-angle lenses will be your bread and butter. These lenses can often produce the images we find most visually fascinating as the lens can often distort what we see with our eyes in real life.

This distortion, however, can be linked to the quality of the lens. With the top wide angle DSLR lenses giving little to no distortion or chromatic aberration whereas the more affordable will see more. You are able to correct for this in editing software.
Wide angle DLSR lenses are available in both prime and zoom lenses with quality and affordability varying between the two. To determine which is for you, first you need to think about what you will be using it for. For example, if you are shooting portraits where you are able to easily move yourself around to capture the shot then a prime lens maybe best. However, if you are shooting a live performance where you are in a fixed position a zoom lens is probably going to be a better option.
Telephoto Lenses
If you are looking to photograph subjects from far away, then a telephoto lens is for you. They are generally lenses that have a focal length of 85mm or longer and like the other lenses they come in both prime and zoom.
When it comes to telephoto lenses though, it is the zoom lenses that are the most popular. This is because the situations that you generally need a telephoto lens require a little bit of flexibility and a zoom lens gives you that.

Zoom telephoto lenses are particularly popular with sports and wildlife photographers as they are able to follow a subject without having to move much themselves. These lenses also tend to have image stabilisation features which can be really helpful. It helps cut down any shaking or vibrations which become more obvious at longer focal lengths.
Standard DSLR Lenses
Your general purpose, all-round and kit lenses are great when you are just starting out. They allow you to do multiple different types of photography with just one or two lenses. This means you can figure out which kinds of photography you are most interested in before buying more specialised lenses. They are also popular with event and wedding photographers where the act of changing lenses can mean missing a potentially amazing shot.
These lenses are generally zoom lenses and because they are built to do multiple different things the overall image quality is not as high as a prime lens. However, there is a huge variety with some even having the ability to go from a wide angle to a long telephoto! Obviously the more you want the lens to do the lower the image quality will be. Nevertheless, it is a great option if you are just starting out.
Portrait DSLR Lenses

If shooting portraits is your jam, then bagging yourself one of these lenses is a no brainer. These lenses are generally prime lenses and so deciding on what kind of portrait you want to capture will help you decide which focal length to get.
In general, a great starting point is to go for a focal length of around 50-85mm. This is because you can capture the soft beauty of a subject while still being able to add some drama and vibrancy.
Fisheye DSLR Lenses
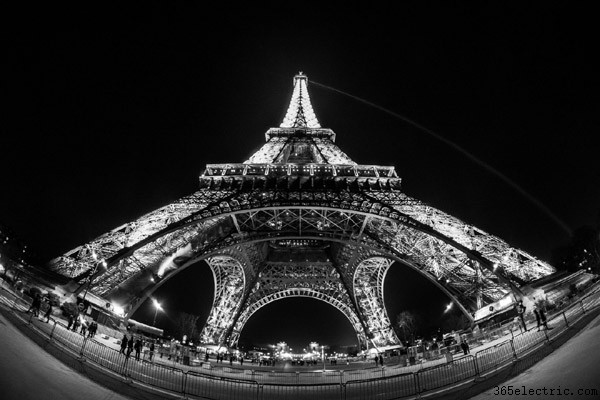

These lenses are ultra-wide-angle lenses and produce a full 180-degree radius image. These types of images are instantly recognisable as they distort the image and make everything look like its in a bubble. These types of lenses are usually prime lenses.
Tilt Shift DSLR Lenses
Also known as perspective-control lenses they allow you to shift and tilt the optical configuration of the lens relative to the sensor. Basically, it means that when you are photographing buildings you can correct for key stoning (an effect that makes buildings appear like they are falling over).
You can also adjust the depth of field without changing the aperture which can be helpful in landscape and product photography. On the other hand, they only have the ability to focus manually.
Other Things to Consider
Distortions
Not all lenses are perfect, and they all have varying degrees of distortion. Prime lenses usually have the least because they do not have to accommodate a range of focal lengths. There are two main types of distortion to be aware of when choosing your lenses:Barrel distortion and Pincushion distortion.
Barrel distortion is when the edges of the image look barrel-sized rather then straight. Pincushion distortion on the other hand is the opposite. It makes the edges bow inwards. You can also get an image that has a mixture of both which is known as a complex distortion.
As technology improves modern zoom lenses are not plagued by distortions as much. Although it is worth noting that these distortions can often be corrected for in photo editing software.
Aberrations
One of the reasons multiple lenses or glass elements are used inside a camera lens is because while a single lens could form an image, it would have aberrations.
Sometime the light that passes through your lens is not all bent in exactly the same way and causes what is known as aberrations or edges of the image that are not coloured correctly. There are some colours that are affected by this more than others and also some lenses. You can often correct for this using editing software though.
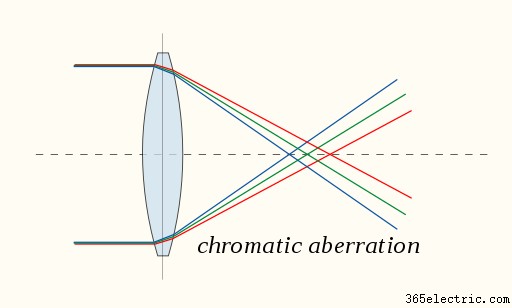
Chromatic aberrations are also diminished when different material lenses are used together in the group, therefore realigning the colors.
Lens Sharpness
Lenses are usually sharpest in the middle and sharpness also isnt the same throughout a lenses zoom range. As I said before, lenses have come a long way now that we use DLSRS, but they are not perfect yet. If you use your lens for many types of projects you will learn its sharpness qualities. One thing in common is lenses are less sharp when the aperture is wide open, so if you are experiencing that issue use a smaller aperture.
Well, that is it for my review of how DSLR lenses work and differ. I hope this article has helped you understand lenses more. As you can see its not all that complicated.
You can learn more about budget friendly lenses for aspiring professional photographers here
